NEW: Updated NCCN MM Guidelines Strengthen Recommendation for Baseline Clonotype ID at Diagnosis.
Covered by Medicare and FDA-cleared, clonoSEQ supports baseline ID assessment to enable subsequent next generation sequencing (NGS)-based MRD tracking. For more info about incorporating clonoSEQ into your clinical practice for MM patients, click here.
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
clonoSEQ helps you take earlier action by clarifying the state of your pediatric and adult ALL patients
FDA-cleared in bone marrow, CLIA-validated in peripheral blood
While remission is a common outcome for ALL patients after initial treatment, most adults and some pediatric patients will relapse.1,2 Regular measurable residual disease (MRD) testing with clonoSEQ can help you measure deep responses and detect potential relapse earlier, which can inform important treatment decisions that may improve your patients’ outcomes.
clonoSEQ offers the deepest level of MRD detection currently available,* so you can make clinical choices with clarity and confidence
Actionable relapse detection
Use clonoSEQ after cellular therapy for earlier detection of relapse in pediatric patients.1
A combined analysis from the ENSIGN and ELIANA in ALL pediatric trials found that MRD detection by clonoSEQ after chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy preceded overt relapse.1
79% of post-infusion samples drawn at 1, 3, and 6 months.
“Our data show that BM NGS-MRD measurements [by clonoSEQ] are the most sensitive biomarker to date for defining risk of relapse after CAR T-cell therapy.”
— Pulsipher et al1
Efficacy predictions
Use clonoSEQ after CAR-T therapy to predict outcomes in pediatric patients.
Further combined analysis from the ENSIGN and ELIANA trials showed that MRD positivity by clonoSEQ at months 3 and 6 post CAR-T therapy was associated with poor overall survival.1
“No one with NGS-MRD >0 detected at these later time points survived without significant additional intervention.”
“No one with NGS-MRD >0 detected at these later time points survived without significant additional intervention.”
— Pulsipher et al1
clonoSEQ is a valuable assessment tool for patients receiving CAR T-cell therapy, providing both prognostic information and allowing for earlier detection of relapse so additional therapies can be planned
Pre-transplant prognosis
MRD status by clonoSEQ before transplant is crucial for prognosis.
In another study of pediatric ALL patients, pre-transplant bone marrow (BM) samples from 41 patients found that MRD detection predicted relapse and overall survival (OS) significantly better than multiparameter flow cytometry (MFC).2
Large differences in 2-year relapse probability were observed between pre-transplant MRD-negative and -positive results by clonoSEQ.2
0%
of patients who were MRD negative before transplant relapsed2
53%
of patients who were MRD positive before transplant relapsed2
“The power of a negative clonoSEQ assay is tremendous for our patients.”
— Dr. Greg Yanik, Pediatric Hematology Oncologist, University of Michigan
Use of clonoSEQ prior to transplant may help you identify risk for relapse after transplant, allowing you to modify their treatment plan as needed
Early response insights
clonoSEQ can identify patients who are likely to have durable remission after chemotherapy.3
In a 2022 study, adult patients who achieved MRD negativity by clonoSEQ (<10-6) at the time of complete response with chemotherapy had durable remissions.3
5-year cumulative incidence relapse rate
0%
for MRD-negative patients3
45%
for MRD-positive patients3
Early MRD negativity detection by clonoSEQ can help identify patients likely to remain in remission
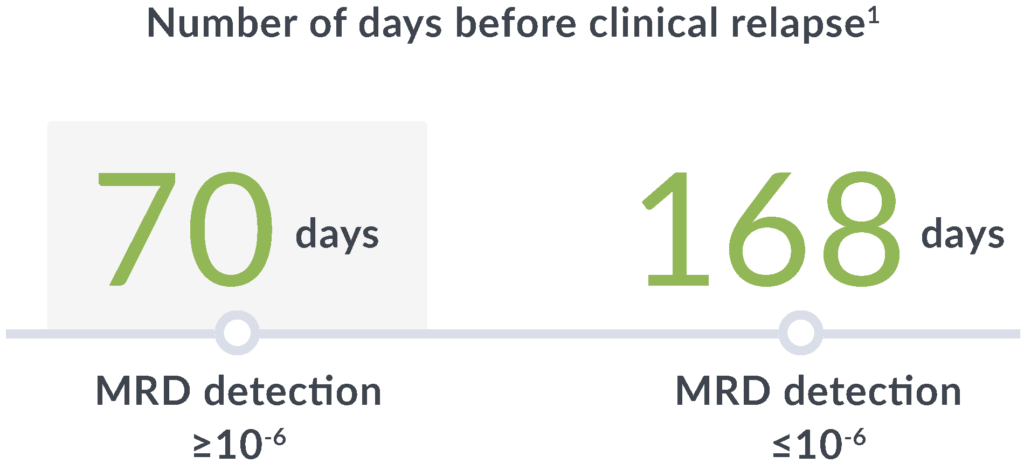
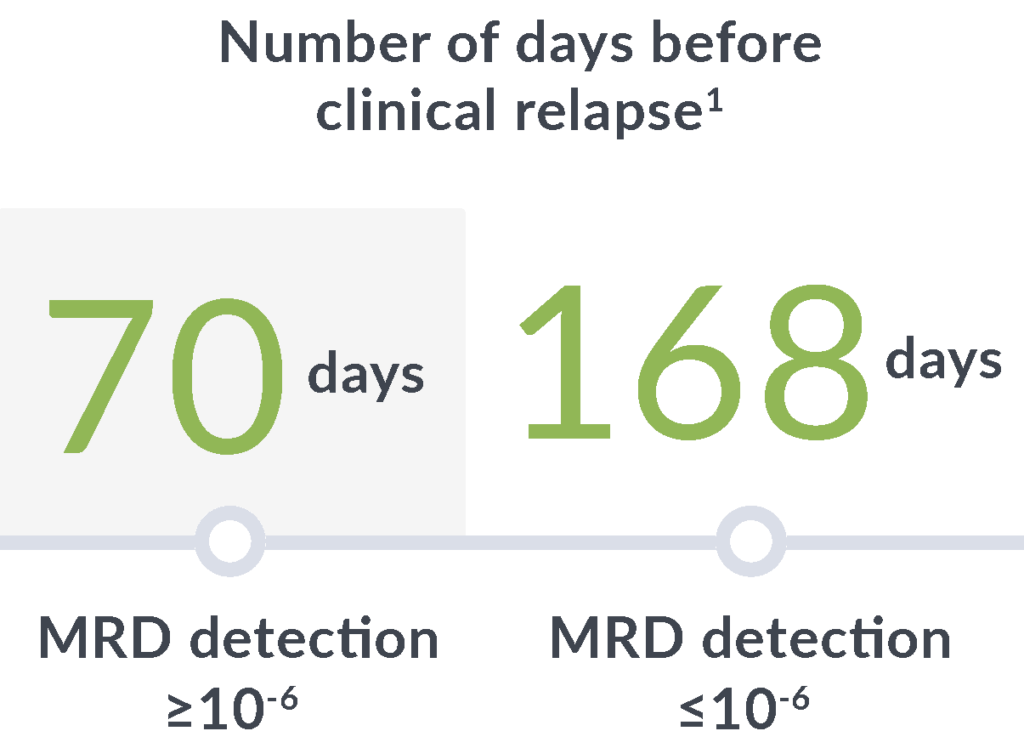
Early relapse prediction
In a study of adults with ALL, MRD positivity by clonoSEQ (≥10-6) at any point after hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) through 100 days was associated with a7:
14x
greater risk of relapse
89
day median lead time
clonoSEQ gives you time to adjust treatment plans before clinical relapse
Pre-transplant foresight
MRD levels measured by clonoSEQ before transplant are associated with relapse risk after transplant.
In a 2023 retrospective study of adult ALL patients, depth of pre-transplant MRD by clonoSEQ distinguished different levels of relapse risk.9
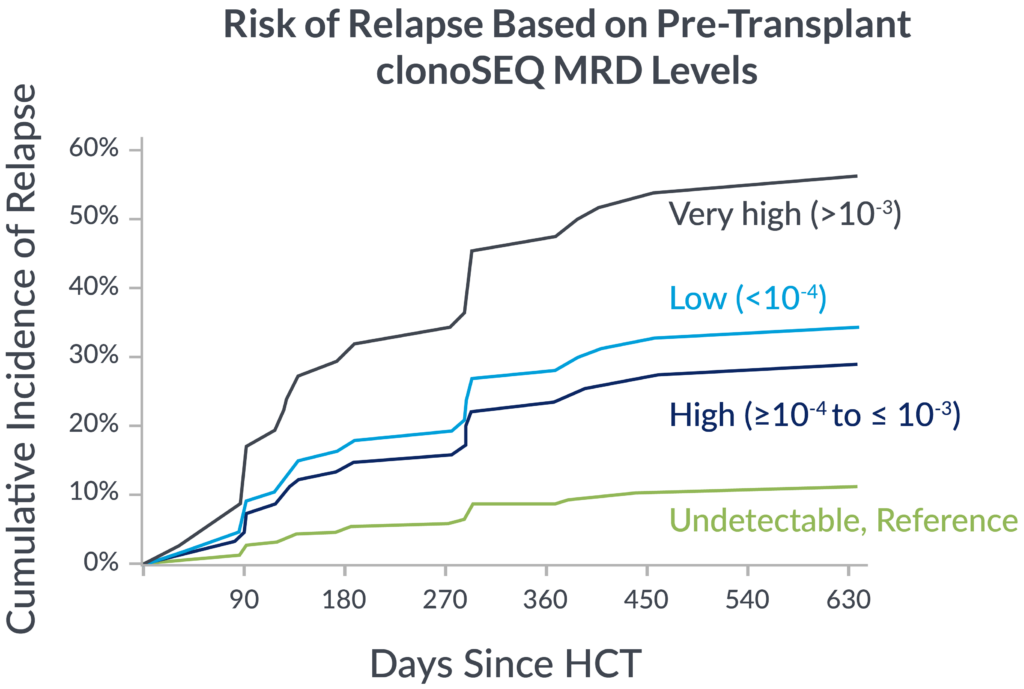
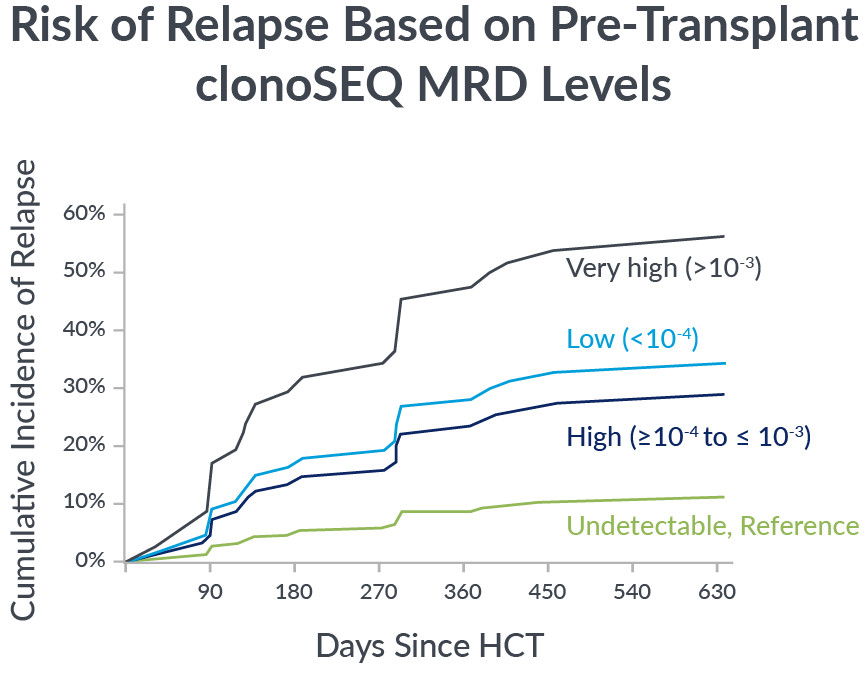
If you’re not measuring MRD with the deep sensitivity of clonoSEQ, you may be missing important insights into your patient’s potential long-term outcomes
Post-transplant insights
Monitoring with clonoSEQ after transplant can identify patients with a strong prognosis.7
~5-year
median survival rate
for 75% of MRD-negative patients (<10-6)7*
median survival rate for 75% of MRD-negative patients (<10-6)7*
~1-year
median survival rate
for 100% of MRD-positive patients (≥10-6)7*
median survival rate for 75% of MRD-negative patients (<10-6)7*
*Samples were collected before day 100 post HCT in 24 patients were evaluated for MRD.7
Gaining insight into your patient’s post-transplant prognosis can help you make future treatment decisions
Convenience without compromise
clonoSEQ allows you to use blood-based testing with confidence.1,8
Research shows that blood samples offer a viable non-invasive alternative to serial BM assessment in ALL.1,8,9
In a study of adult patients receiving cellular therapies, a strong correlation between clonoSEQ results were observed from paired peripheral blood (PB) and BM samples (89% concordance).8
clonoSEQ allows you to frequently monitor for subtle changes in your patient’s disease with a simple, minimally invasive blood-based MRD test
More powerful than MFC
clonoSEQ fills in the gaps that MFC misses.
Multiple studies show that clonoSEQ routinely detects disease that MFC misses. This can help you make more informed treatment decisions for your patients with ALL that may impact survival.
Percentage of patients who were MRD negative by MFC but had residual disease detected by clonoSEQ3,4
46%
Adult ALL
39%
Pediatric ALL
Deeper sensitivity with clonoSEQ reveals more about your patient’s specific disease status and outcomes
Leverage the clinical insights of clonoSEQ MRD testing across treatment phases in ALL
Clinical practice guidelines and clinical trial data support regular MRD testing at multiple timepoints during and after active treatment.
Induction
Initiating clonoSEQ MRD assessment after induction can help inform subsequent treatment decisions
Transplant
Testing your patient with clonoSEQ before and after transplant can help you understand their risk of relapse2
Second-Line and Beyond
clonoSEQ can help you detect early relapse after CAR T-cell therapy and determine next steps for certain patients
Monitoring
Post-treatment monitoring with clonoSEQ can help detect relapse earlier than MFC, giving you more time to take action
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) recommend MRD testing in:
- Pediatric ALL patients at induction and before/after transplant5
- Adult ALL patients at induction, before/after transplant, in patients with complete molecular remission, and at additional points in treatment plans6
Coverage throughout a patient’s treatment journey
clonoSEQ is well covered, regardless of a patient’s insurance.
- National Medicare coverage for ALL patients at multiple testing timepoints with most patients paying $0 out-of-pocket
- Positive coverage policies from the largest national private insurers†
View the clonoSEQ ALL Clinical Data Summary
Ready to get started with clonoSEQ?
ctDNA MRD Testing Now Included in DLBCL Clinical Practice Guidelines
Clinical practice guidelines now include ctDNA MRD testing after frontline therapy for PET-positive DLBCL patients.
clonoSEQ is the only commercially available, Medicare-covered, ctDNA MRD test for DLBCL patients.
NGS, next-generation sequencing.
*Given sufficient sample material.
†Medicare advantage patients may have out-of-pocket costs.
About the studies
Concordance pediatric ALL
143 patients enrolled in the ENSIGN and ELIANA studies had 1771 MFC samples analyzed. Patients were pediatric and young adult patients with CD19+ relapsed or refractory B-cell ALL who were treated with tisagenlecleucel (median follow-up 38.4 months). MRD was measured at various time points after achieving remission (BM at 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months).1
This study evaluated a cohort of patients with ALL enrolled in COG ASCT0431/PBMTC ONC051 who were undergoing HCT to determine if the increased sensitivity of NGS–MRD better identifies pre- and post-HCT relapse risk than MFC.2
Concordance adult ALL
In a study of 237 samples from 29 adult B-cell ALL patients before and after allo-HCT, the quantification of MRD was assessed by the LymphoSIGHT platform. Samples were taken at diagnosis or relapse were studied for immunoreceptor clonality and pre- and post-molecular MRD.7
This study evaluated 62 patients with B- or T-ALL undergoing HCT or CAR T-cell therapy. MRD was performed on paired prospectively collected PB and BM samples at prespecified time points to assess the effectiveness of blood monitoring vs BM in ALL patients receiving cellular therapies.8
Adult ALL vs MFC
A retrospective study of 74 Ph-negative ALL patients who achieved a complete remission following frontline therapy. MRD was evaluated by MFC (10-4) and by
clonoSEQ (10-6).3
Pediatric ALL vs MFC
This study evaluated MRD in the BM of 579 pediatric ALL patients from the Children’s Oncology Group trials AALL0331 or AALL0232. The threshold for MFC and clonoSEQ was 10-4 (1:10,000). MRD was assessed post-induction.4
This page is intended for a US-based audience.
clonoSEQ® is available as an FDA-cleared in vitro diagnostic (IVD) test service provided by Adaptive Biotechnologies to detect measurable residual disease (MRD) in bone marrow from patients with multiple myeloma or B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) and blood or bone marrow from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Additionally, clonoSEQ is available for use in other lymphoid cancers and specimen types as a CLIA-validated laboratory developed test (LDT). To review the FDA-cleared uses of clonoSEQ, visit clonoSEQ.com/technical-summary.
References:
- Pulsipher M, et al. Blood Cancer Discov. 2022;3:1-16.
- Pulsipher M, et al. Blood. 2015;125(22):3501-3508.
- Short N, et al. Blood Adv. 2022;6(13):4006-4014.
- Wood B, et al. Blood. 2018;131(12):1350-1359.
- Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia V.3.2024. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2023. All rights reserved. Accessed January 23, 2024. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org. NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.
- Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia V.3.2023. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2023. All rights reserved. Accessed January 23, 2024. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org. NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.
- Logan A, et al. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20(9):1307-1313.
- Muffly L, et al. Blood Adv. 2021;5(16):3147-3151.
- Liang E, et al. Blood Adv. 2023;7(14):3395-3402.