clonoSEQ is now covered by Medicare for MCL patients.
It is the first Medicare-reimbursed MRD test for patients with MCL and is clinically available as a CLIA-validated LDT.
For more information about incorporating clonoSEQ into your clinical practice for MCL patients, click here.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
clonoSEQ informs a more personalized approach to clinical management of CLL
FDA-cleared and CLIA-validated in bone marrow and peripheral blood
Patients with newly diagnosed CLL may not require immediate treatment. While the decision to initiate therapy relies on multiple clinical factors, patients will eventually initiate treatment on either a fixed-duration or a newer response-dependent regimen.
Serial monitoring with clonoSEQ provides the deepest view of your patient’s disease during and after treatment, so you can make informed decisions about their care
Enhanced insights
Monitor disease kinetics more precisely than other assessment methods1,2
In the CLL14 study, measurable residual disease (MRD) was assessed in the peripheral blood by multiparameter flow cytometry (MFC) at 10-4 and at a deeper level of sensitivity (10-6) with clonoSEQ.
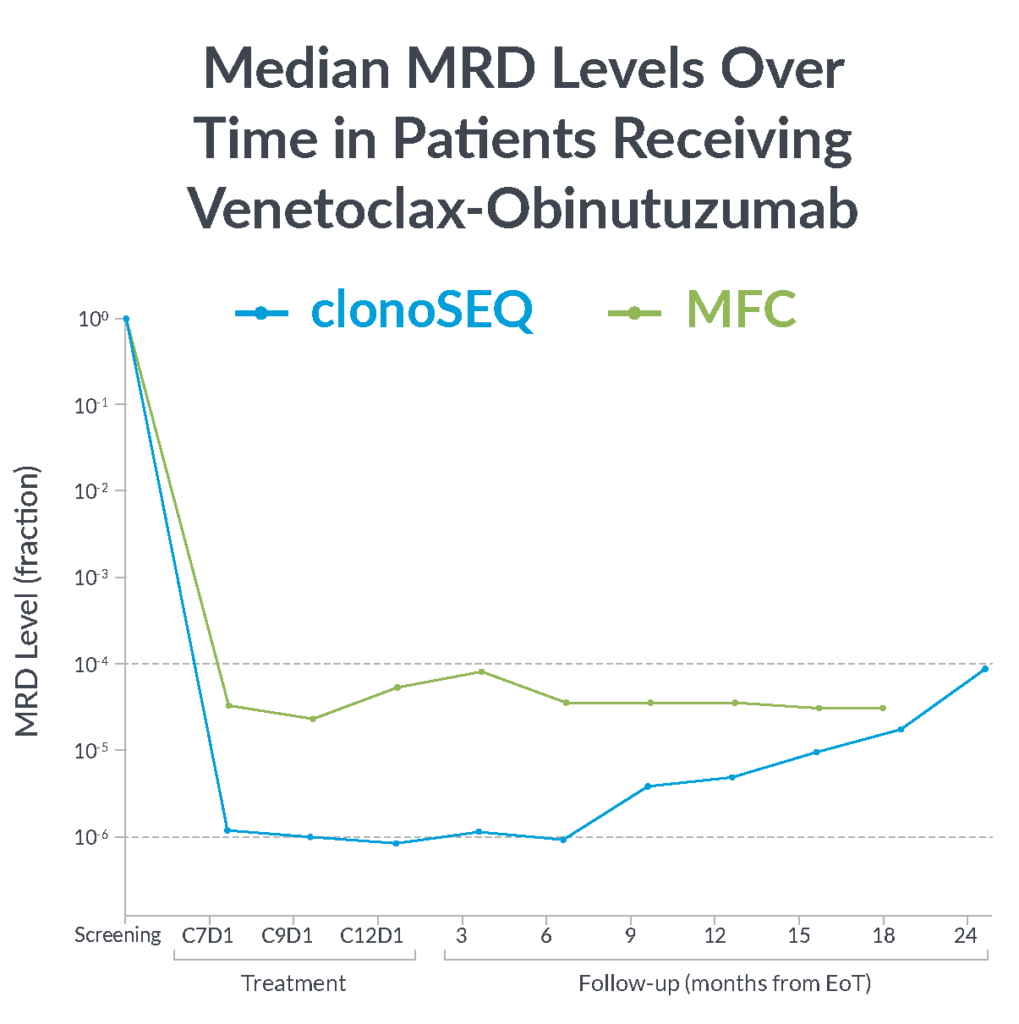
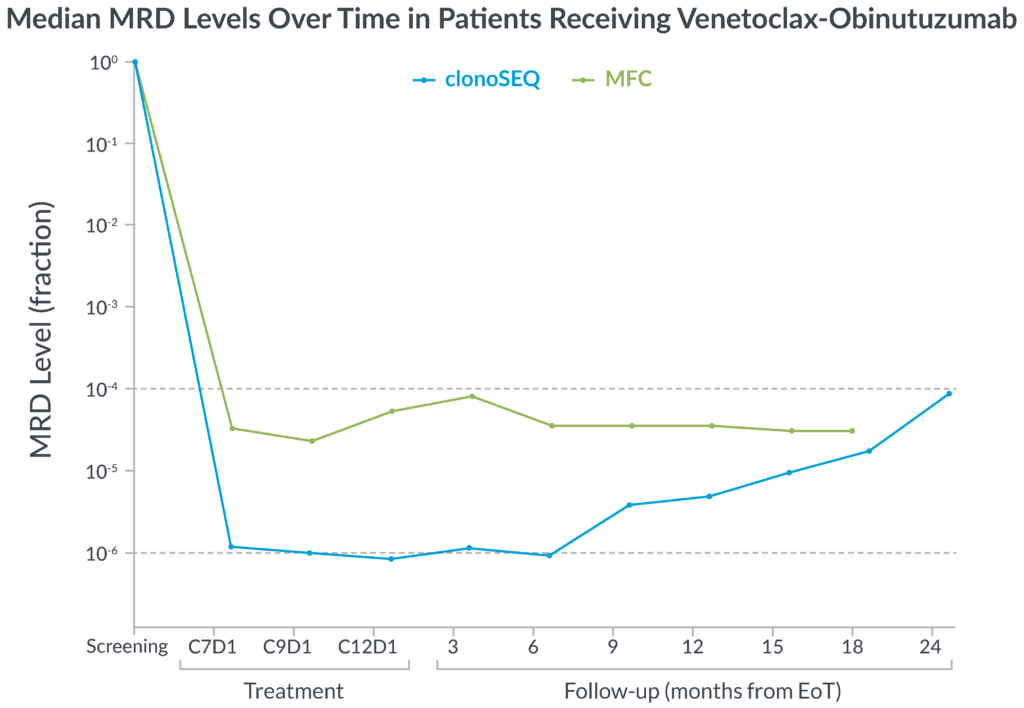
MFC missed the slow but steady increase of MRD that was detected by clonoSEQ1
clonoSEQ offers greater insight into disease kinetics than MFC, allowing you to have a better understanding of your patient’s disease burden1
Magnitude of MRD response
A clinically informative measure worth consideration.
In one study of previously-untreated CLL patients, magnitude of reduction in MRD by clonoSEQ predicted MRD resurgence.3
This trial was primarily designed to assess rate of undetectable MRD (U-MRD) with 8-24 cycles of zanubrutinib, obinutuzumab, and venetoclax therapy. Patients with two consecutive U-MRD tests two cycles apart could discontinue therapy.3
Rate of MRD resurgence at 1 year3
5%
in patients who had a >400-fold reduction in MRD by cycle 5
75%
in patients who had a <400-fold reduction in MRD by cycle 5
Large reductions in MRD, only revealed fully by clonoSEQ, provide meaningful clues to prognosis3
Depth matters
Greater depth, better progression-free survival (PFS) with clonoSEQ.
In a study designed to determine the impact of depth of MRD response on PFS, patients with MRD <10-5 had better outcomes than patients with higher levels of MRD ≥10-5.4
Achieving MRD negativity with clonoSEQ was prognostic of 3-year overall survival (OS)2

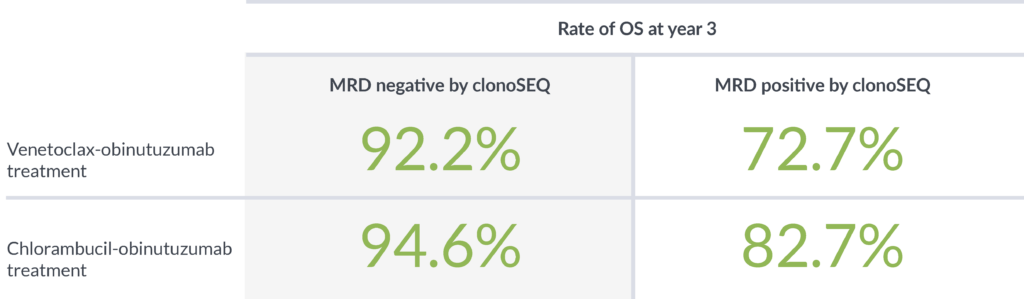
clonoSEQ shows that depth of response has a meaningful impact on PFS and OS4,5
clonoSEQ detected what MFC could not4,5
In a recent study, 62 CLL patients who received first-line fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) therapy were identified as MRD negative by MFC (10-4).
79%
of patients who were MRD negative by MFC (10-4) had residual disease detected by clonoSEQ (10-6)6
79%
of patients who were MRD negative by MFC (10-4) had residual disease detected by clonoSEQ (10-6)6
In another study of 35 patients identified as MRD negative by MFC, clonoSEQ showed a deeper level of molecular response.3*

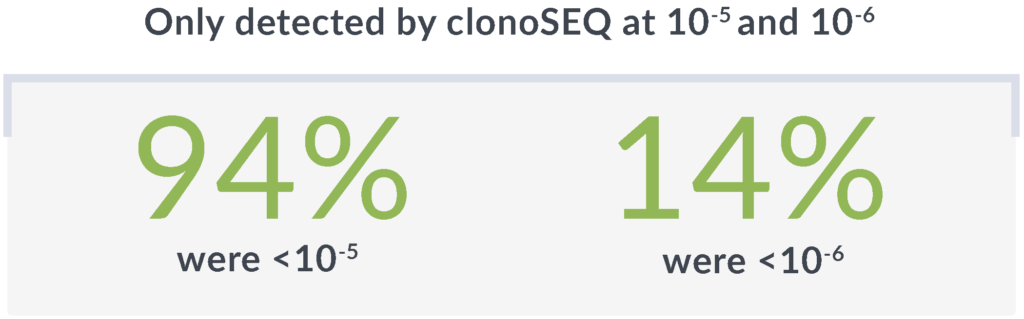


Rely on the unmatched sensitivity† of clonoSEQ to detect disease that other methods may miss
FDA cleared in bone marrow and peripheral blood for CLL with high concordance between the two.5
85% concordance between clonoSEQ assessment via bone marrow (BM) and peripheral blood (PB) was demonstrated.
Leverage the clinical insights of clonoSEQ MRD testing across treatment phases in CLL
Clinical practice guidelines and clinical trial data support regular MRD testing at multiple timepoints during and after treatment.
Fixed-duration therapy
Predict long-term patient outcomes following fixed-duration therapy
End of treatment
Monitor for potential relapse off treatment to inform next steps1
Response-adapted therapy
Inform treatment discontinuation decisions depending on depth and durability of response3
Surveillance
Significant association between PFS and clonoSEQ MRD status was seen in both blood and bone marrow in follow-up testing5
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) recommend MRD testing in CLL patients at end of treatment.7
clonoSEQ is featured in the National Community Oncology Dispensing Association (NCODA) Positive Quality Intervention for CLL.8
Explore an overview of the utility of clonoSEQ in assessing MRD in patients with CLL.
Coverage throughout a patient’s treatment journey
clonoSEQ is well covered, regardless of a patient’s insurance.
- National Medicare coverage for CLL patients at multiple testing timepoints with most patients paying $0 out-of-pocket
- Positive coverage policies from the largest national private insurers†
View the clonoSEQ CLL Clinical Data Summary
Ready to get started with clonoSEQ?
ctDNA MRD Testing Now Included in DLBCL Clinical Practice Guidelines
Clinical practice guidelines now include ctDNA MRD testing after frontline therapy for PET-positive DLBCL patients.
clonoSEQ is the only commercially available, Medicare-covered, ctDNA MRD test for DLBCL patients.
*Threshold of sensitivity was 10-4 with MFC and 10-6 with clonoSEQ.
†Given sufficient sample material.
EoT, end of therapy.
About the studies
Prognosis and Serial Monitoring
In the phase 3, open-label, randomized CLL14 study, Al-Sawaf, et al evaluated rates of MRD negativity and OS after one-year fixed-duration treatment of Ven-Obi in patients with previously untreated CLL.2
In a multicenter, single-arm phase 2 trial CLL patients received BOVen in 28 day cycles and discontinued after 8-24 cycles when prespecified MRD-negative (by MFC) criteria were met in PB and BM. clonoSEQ was used to measure MRD kinetics (decrease in MRD from baseline to day 1 of cycle 5 with a reduction to 1/400th of baseline value chosen as the optimal cutoff [ΔMRD400]).3
vs MFC
MRD was assessed using 4-color MFC (10-4) and clonoSEQ (10-6) in newly diagnosed CLL patients who received up to 6 courses of standard FCR conducted at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (NCT00759798).4
Surveillance
MRD was assessed in 62 previously untreated CLL patients who received therapy with FCR. These patients were initially determined to be U-MRD by 4-color MFC at an MRD threshold of 10-4. From these patients, 57 BM samples were evaluated at the end of treatment by clonoSEQ.4,5
This page is intended for a US-based audience.
clonoSEQ® is available as an FDA-cleared in vitro diagnostic (IVD) test service provided by Adaptive Biotechnologies to detect measurable residual disease (MRD) in bone marrow from patients with multiple myeloma or B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) and blood or bone marrow from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Additionally, clonoSEQ is available for use in other lymphoid cancers and specimen types as a CLIA-validated laboratory developed test (LDT). To review the FDA-cleared uses of clonoSEQ, visit clonoSEQ.com/technical-summary.
References:
- Al-Sawaf O, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(9):1188-1200.
- Al-Sawaf O, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(36):4049-4060
- Soumerai J et al. Lancet Haematol. 2021;8(12):e879-e890.
- Thompson P, et al. Blood. 2019;134(22):1951-1959.
- clonoSEQ®. [technical summary]. Seattle, WA: Adaptive Biotechnologies; 2020.
- Data on file. Adaptive Biotechnologies. 2022.
- Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma V.1.2024. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2023. All rights reserved. Accessed January 23, 2024. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go to NCCN.org. NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use of application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use.
- National Community Oncology Dispensing Association (NCODA). Positive Quality Interventions (PQIs). Accessed January 18, 2024. https://www.ncoda.org/pqis/